题目
【见附件,来源水群】
方法1
每个时间段有十九种状态且每个状态的概率是之前时间的状态的函数,直觉上要用动态规划。
#include<iostream>
#include<chrono>
using namespace std;
const int tmax = 6000, lenmax = 18;
double pot[tmax + 1][lenmax + 1]; //储存所有状态
int main()
{
auto RUNTIME1 = chrono::system_clock::now();
pot[0][12] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= tmax; ++i) { //从初始态逐步计算到目标时间
for (int j = 1; j < lenmax; ++j) { //每个状态通过题目给出状态转移的方法进行计算
double p = pot[i - 1][j];
if (j < 9) {
pot[i][j - 1] += p * 0.4;
pot[i][j + 1] += p * 0.6;
}
else if (j == 9) {
pot[i][j - 1] += p * 0.5;
pot[i][j + 1] += p * 0.5;
}
else {
pot[i][j - 1] += p * 0.6;
pot[i][j + 1] += p * 0.4;
}
}
}
const int term = tmax / 60;
double ans1 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= term; ++i) {
ans1 = 0;
int T = i * 60;
for (int j = 1; j < lenmax; ++j) {
ans1 += pot[T][j];
}
cout << i << "min后持续的概率: " << ans1 << endl;
}
double ans2[tmax + 1] = { 0 };
for (int j = 1; j <= term; ++j) {
int I = j * 60;
for (int i = 1 + (j - 1) * 60; i <= I; ++i) {
ans2[j] += (pot[i][0] + pot[i][lenmax]) * i;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= term; ++i) {
cout << "第" << i << "分钟内的期望子式: " << ans2[i] << endl;
}
double ans3 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= term; ++i) {
ans3 += ans2[i];
}
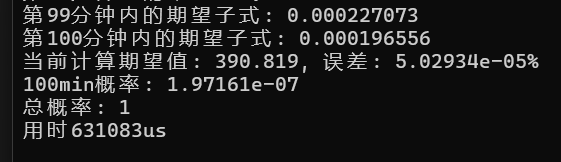
cout << "当前计算期望值: " << ans3 << ", " << "误差: " << ans2[term] / ans3 * 100 << '%' << endl;
cout << term << "min概率: " << ans1 << endl;
double ans4 = ans1;
for (int i = 1; i <= tmax; ++i) {
ans4 += pot[i][0] + pot[i][lenmax];
}
cout << "总概率: " << ans4 << endl;
auto RUNTIME2 = chrono::system_clock::now();
cout << "用时" << (RUNTIME2 - RUNTIME1).count() << "us" << endl;
}
通过对100min内期望的计算可以猜测期望子式和收敛于某个值,该值即为数学期望。表达式有无数个子式。
耗时约0.6s,在8min时约70ms,应该不会超时,不作进一步优化。
结果

方法2
用矩阵描述状态转移(状态转移矩阵)。
M=zeros(19,19)
for i=2:9
M(i-1,i)=0.4
M(i+1,i)=0.6
end
M([9,11],10)=0.5
for i=11:19
M(i-1,i)=0.6
M(i+1,i)=0.4
end
初始状态为:
S=zeros(19,1)
S(13)=1
第n秒各状态的概率:
M^n*S
要求停止的数学期望,即状态1和19的和乘以时间n:
Select=zeros(1,19)
Select([1,19])=1
Select*M^n*S
求极限
由于矩阵的指数不能为sym类型,先对角化:
[V,D]=eig(M)%MV=VD,M=VDV^-1,M^n=VD.^nV^-1
求极限:
syms n
f=Select*V*D.^n*V^-1*S
limit(f,n,inf)%结果为0
对该数列求极限为0,可能收敛。
求和的极限:
symsum(f,n,inf)
值和方法1完全不同。检查发现在10s内的结果完全相同,随时间延长到60s时已出现在千分位的不同,到480s时已经完全不同。
误差原因
可能由于对角化时对数位的圆整,或在初始状态后发生了显示0的元只是很小的浮点型的情况。

comment 评论区
star_outline 咱快来抢个沙发吧!